Across industries and sectors, we must acknowledge that cybersecurity threats are evolving fast, and with relentless sophistication. Therefore, the foundational principle of effective defense remains: you cannot safeguard what you do not know exist.
Enterprises lacks insight in to the technical landscape to make informed decisions
As organizations’ technical and digital footprints grow in complexity and scale, the demand for insight to make informed decisions increases proportionately.
Insufficient technical and digital landscape insight leads to significant risks,
- Lack of technical standardization across an organization can lead to vulnerabilities and weaknesses due to inconsistent configuration practices, often a result from poorly defined or non-enforced configuration management processes. Misconfigured settings can create security holes, such as open ports, weak encryption, or inadequate authentication mechanisms, increasing the attack surface and potential for unauthorized access. Hardware devices running outdated firmware can also have exploitable vulnerabilities and weaknesses.
- Incomplete or outdated inventories of assets make it difficult to manage and secure all components effectively, allowing unmanaged assets to become entry points for attackers. Poorly defined processes around Asset and Configuration Management further increase the risk of misconfigurations and security incidents.
- A lack of training and awareness among staff regarding best practices in asset and configuration management can lead to human errors, resulting in misconfigurations, unpatched systems, and other vulnerabilities and weaknesses. Difficulty integrating various tools and systems for Asset and Configuration Management can create gaps in coverage and visibility, further increasing the risk of security incidents.
- Manual processes, prone to human error and inadequate for scaling with organizational growth, can result in inconsistent application of security policies and delayed responses to threats. The lack of automation raises the potential for security breaches.
To effectively address the aforementioned and other, potential risks, a robust framework for robust asset and configuration insight is essential.
Enter: Asset and Configuration Management
Organizations are facing growing challenges in managing their digital assets and configurations, the risks within cyber and information security vulnerabilities and weaknesses are high. The solution? – Asset and Configuration Management.
Defining Asset and Configuration Management
Asset and Configuration Management is not merely an operational task, but a necessity that lays the foundation to make informed decisions and fortifying the cyber posture. Asset Management is a discipline designed to continuously discover, inventory, monitor, track, and manage an organization’s assets. The term “Asset” encompass hardware, software, data, and network components that form the backbone of the organization’s infrastructure. Configuration Management is a complementary discipline that ensures the consistency and integrity of an organization’s digital environment by systematically identifying, documenting, and controlling all configuration items. The configuration items include hardware, software, firmware, and network devices that interact within the organization’s digital and technical infrastructure. Configuration Management involves maintaining records of each configuration item’s configurations and their interdependencies (to the appropriate level of detail), continuously updating and ensuring the records reflect any changes made.
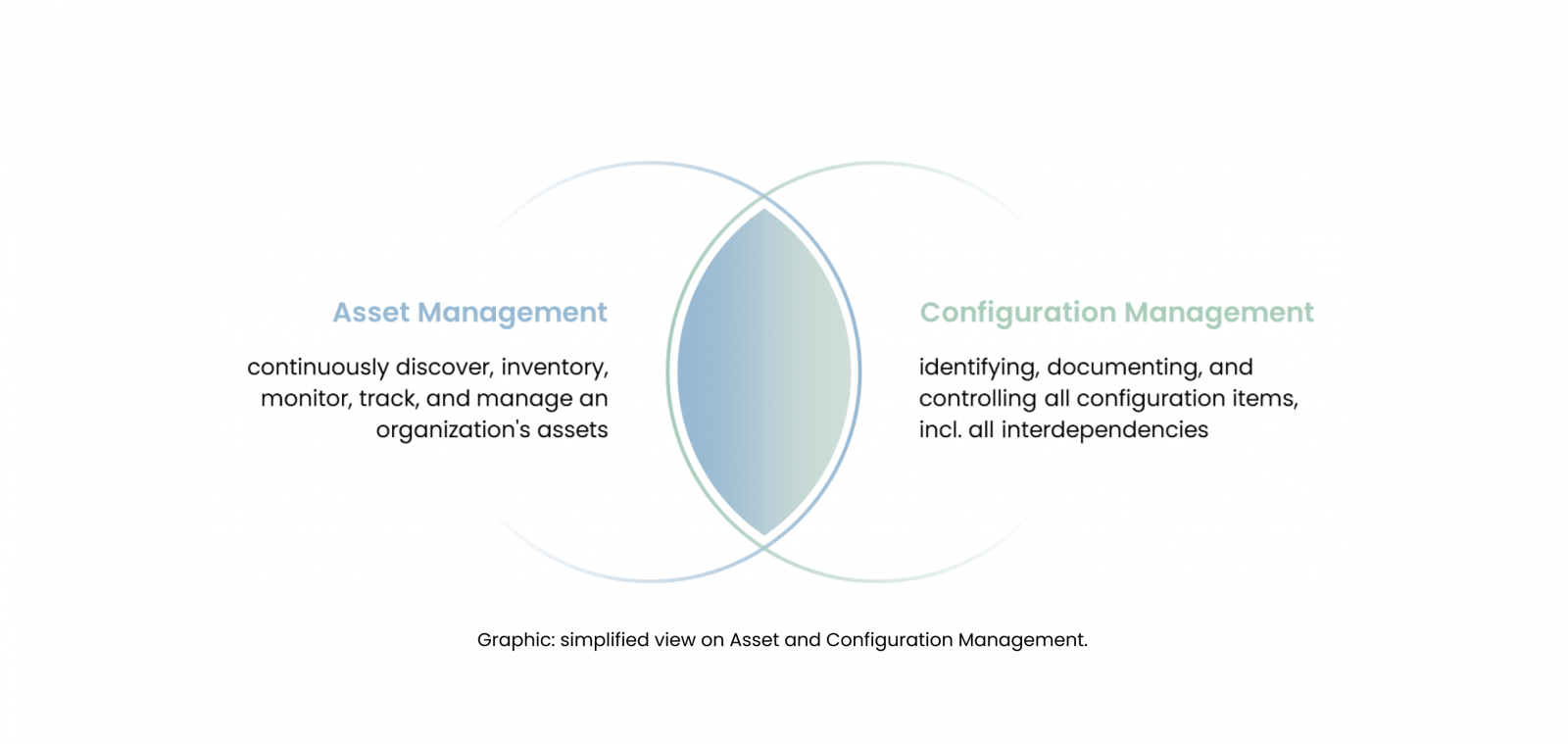
The primary objectives of Asset and Configuration Management is to understand what assets are present, determine their functions, and identify and remediate any gaps in their safeguarding; deviations from set standards across assets and their content. Asset and Configuration Management not only supports efficient problem resolution and system stability, but also strengthens security and compliance by ensuring all modifications are tracked and authorized accordingly. Together, Asset and Configuration Management provide a strong frame for effectively managing the digital and technical resources of an organization.
The components of robust Asset and Configuration Management
Continuous discovery
Continuous Discovery is a crucial, ongoing process that involves identifying all assets within an organization. By employing automated tools to scan and map out devices, applications, and services, it ensures comprehensive visibility. A proactive approach safeguards that no asset remains hidden, and connected shadow equipment is absolved, thus effectively eliminating potential (previously-) unknown entry points for cyber threats.
Inventory and classification
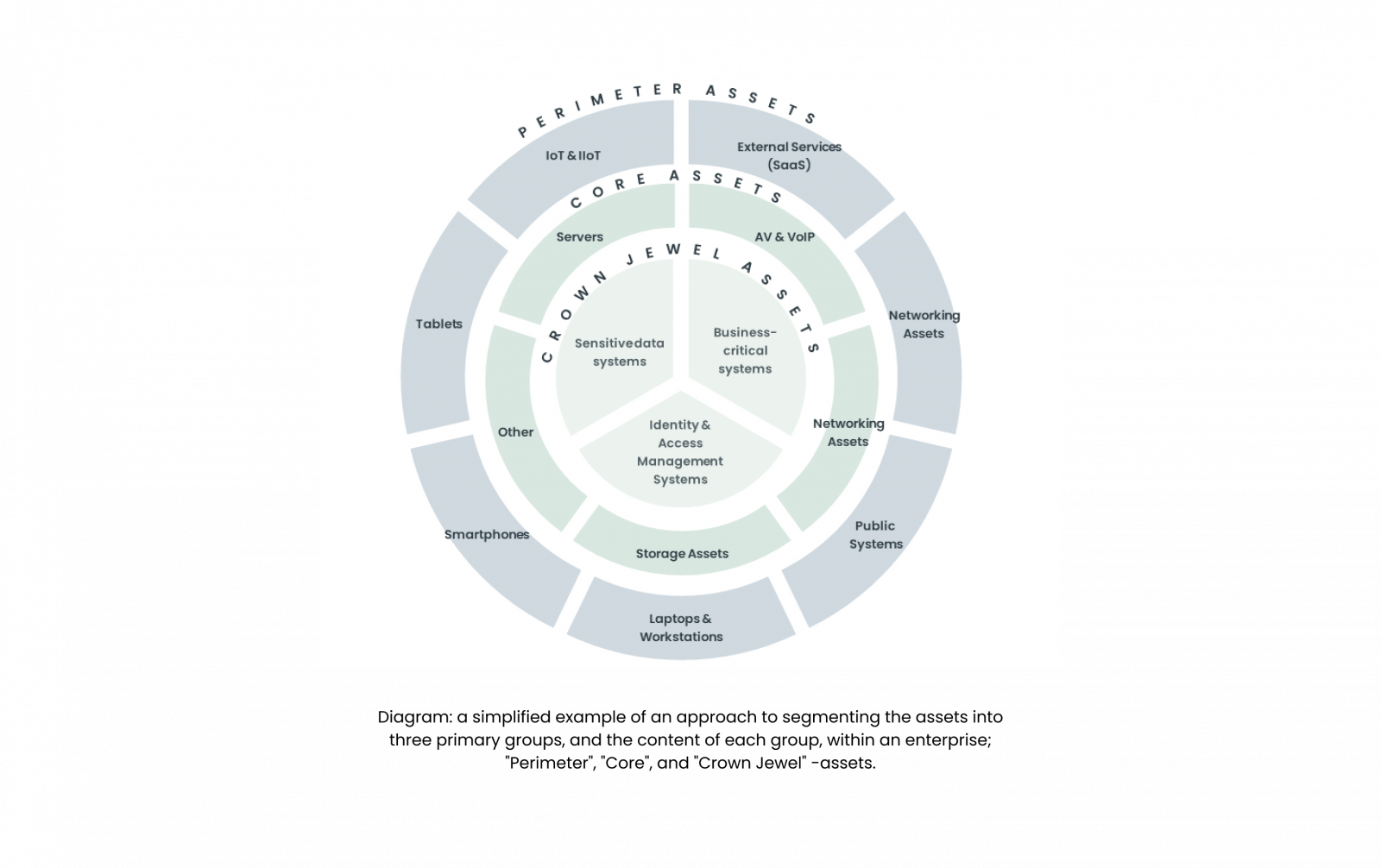
Creating an inventory and classification approach for asset management is critical for ensuring security and operational efficiency. This involves cataloging all assets and categorizing them by type, importance, and risk level. Each asset should be assigned an owner responsible for its security and maintenance. Classification of assets aids in prioritizing those that are critical to business operations and require stringent security measures. Additionally, it is beneficial to consider if asset grouping can enhance your organizational processes. Grouping by system can streamline ownership responsibilities, while grouping by unit profile (/touch points/location & importance) within the enterprise, such as perimeter, core, or crown jewel assets, can facilitate the assignment of threat levels to each group. This approach enables more informed decision-making on cyber risk, security measures and resource allocation.
Monitoring and management
Effective asset and configuration management isn’t a set-and-forget activity; it requires ongoing monitoring and recurring, proactive management. Continuous monitoring solutions are essential for tracking asset location, performance, usage, and compliance. This can be achieved by implementing monitoring at the network layer while approaching the activity via both active and passive asset discovery mechanisms. Additionally, active management involves conducting regular audits and assessments to identify vulnerabilities and ensure timely updates. These practices collectively help maintain the integrity and efficiency of asset management systems.
Tracking and reporting
Within tracking and reporting is the activities focused on maintaining logs, which are crucial for continuous tracking of asset states and conditions, and subsequent. By continuously logging, organizations can generate reports that support compliance audits, technical security assessments, and strategic planning.
Tracking alone is insufficient without the reporting that transforms raw data into actionable insights. The process involves generating reports that provide a holistic view of the asset landscape, including the status, performance, and security posture of each item. Reports should be tailored to meet the needs of various stakeholders, from IT/OT managers who require granular details, to executives who need high-level summaries for strategic decision-making. Advanced reporting capabilities enable organizations to identify trends, uncover vulnerabilities, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. The reports can highlight discrepancies, such as unauthorized changes or deviations from standard configurations, allowing for timely remediation. Automated reporting tools can also schedule regular report generation, ensuring that the information is always current and accessible.
Integrating analytics into the reporting process further enhances its value. Predictive analytics can forecast potential issues before they arise, while historical analysis provides insights into recurring problems or areas for improvement. By applying this approach, it would be possible to supports the organization in ensuring regulatory and strategic requirements are met efficiently, and not only enhancing the visibility and control over assets.
Automated remediation
Automated remediation is a critical component in modern Asset and Configuration Management, leveraging automation to promptly address identified security gaps. By ensuring that assets are continuously updated with the correct configurations, software versions, etc. organizations can maintain robust security postures with less human interaction. This process includes adhering to approved standards for operating systems, application variants, and unit hardening, thereby ensuring consistent and secure asset configurations. Automated remediation encompasses a variety of (sub-)tools, including patch management systems, automated configuration adjustments, and, in general, an opportunity to incorporate SOAR solutions (Security Orchestration Automation and Response). The proposed approach not only reduces the time required for remediation but also minimizes the risk of human errors inherent in manual processes and procedures.
The strategic importance of robust Asset and Configuration Management
Enhanced visibility and control
Asset and Configuration Management provide a holistic view of the organization’s technical and digital landscape, encompassing hardware, software, data, and network components. A comprehensive overview enables teams to identify the interdependencies and relationships between relevant assets and configurations, ensuring complete transparency. The visibility and insight enables proactive management, allowing organizations to identify potential issues before they escalate into major incidents. By continuously monitoring, and managing assets and configurations, organizations can swiftly respond to emerging threats, minimizing downtime and safeguarding sensitive information.
Moreover, the detailed and up-to-date data collected through these management processes facilitates informed decision-making. Senior leaders can make strategic choices based on accurate, in-depth asset data, optimizing resource allocation, and enhancing operational efficiency. With enhanced visibility and control of asset and their configurations, organizations can navigate the complexities of their digital landscapes with confidence, ensuring resilience and agility.
Risk reduction
Asset and Configuration Management are critical processes that help mitigate these risks by providing comprehensive oversight and control over an organization’s technology environment.
By managing and monitoring assets and configurations effectively (-and tightly integrating the Asset and Configuration Management with SOC operations, including SIEM and SOAR), organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches, operational disruptions, and financial losses. Accurate and current records of assets support the operational teams by quickly pinpointing issues, minimizing downtime, and preventing costly incidents. A proactive approach not only protects sensitive data but ensures continuous and reliable business operations.
Resource optimization
In organization’s constant quest for operational efficiency and strategic growth, optimizing resource utilization is in focus. Asset and Configuration Management is an ideal opportunity for business leaders in achieving this goal by enhancing the way organizations manage technical and digital resources.
Effective Asset and Configuration Management enable organizations to prioritize their resources towards the most critical security needs. By maintaining a clear and comprehensive view of all assets and configurations, decision-makers can allocate resources more effectively, ensuring that the most significant risks and vulnerabilities are addressed first. This strategic allocation of resources not only enhances security but also maximizes the return on investment for digital expenditures.
Compliance and governance
Asset and Configuration Management stand as pillars of an organization’s digital / IT strategy. The processes set out from a compliance and governance perspective not only ensures operational efficiency but also plays a central role in adhering to industry regulations and enhancing overall governance.
Regulations such as NIS2, DORA, CER, and other industry-specific standards mandate stringent controls over digital assets and configurations. Asset and Configuration Management enable organizations to meet these regulatory requirements by maintaining precise and up-to-date records of all assets, ensuring that they comply with necessary security and operational standards.
Establishing clear accountability for asset security is a cornerstone of good governance. Asset and Configuration Management define roles and responsibilities for managing digital assets, ensuring that there is a clear line of accountability. This not only enhances governance but also fosters a culture of responsibility and vigilance within the organization.
Implementing an effective Asset and Configuration Management strategy
Ensure support from key stakeholders- and senior management
Achieving senior management and key stakeholder’s support is first and foremost pivotal to the success of an Asset and Configuration Management strategy.
The following areas should be considered when ensuring the backing of senior management and key stakeholders,
- Clearly demonstrate how the strategy aligns with the organization’s overall business objectives. Show how it can drive efficiency, reduce costs, and mitigate risks. Extract and apply relevant content from this article, above.
- Highlight the tangible and intangible benefits of Asset and Configuration Management, such as improved decision-making, enhanced compliance, and increased operational as well as cyber resilience.
- Prepare a business case that includes ROI calculations, cost-benefit analysis, and potential risks of not implementing the strategy.
- Involve key stakeholders and senior management early in the planning process. Regular updates and open communication channels will help in addressing concerns and incorporating feedback.
- Identify and deliver quick wins to build momentum and demonstrate early value. The quick wins can be pilot projects or small-scale, MVP implementations that provide immediate benefits.
Establish clear policies, processes and procedures
Establish clear policies, processes, and procedures to ensure consistency, compliance, and efficiency. Ensure sign-off by senior management and key stakeholders, before initiating the work.
Start by by defining a policy that outlines the scope, objectives, and governance of asset and configuration management (or multiple policies, depending on boundaries and guardrails). The policy(/-ies) should specify roles and responsibilities, ensuring accountability at every level.
Next, develop detailed processes that translate these policies into actionable steps. These processes should cover the entire asset lifecycle, from acquisition to disposal, and include configuration management activities like identification, control, status accounting, and verification.
Finally, establish standardized procedures to support these processes, providing step-by-step instructions for tasks such as inventory management, asset tracking, and change management, or even better: power the procedures by automation.
Adopt advanced tools and technologies
Leveraging advanced tools and technologies will aid in the streamlining of the operational procedures, and significantly enhance the accuracy of the Asset and Configuration Management database. To begin, organizations should assess their specific requirements, such as asset tracking, configuration monitoring, and compliance reporting. Evaluating and comparing available tools based on factors like integration capabilities, scalability, and user-friendliness is essential in this step (consider if any of the existing tools can support your journey).
Next, ensuring compatibility of the selected tools with the existing IT/OT infrastructure is crucial for seamless integration. Utilizing APIs and connectors facilitates smooth data flow between new tools and legacy systems. Automation plays a key role in enhancing efficiency; automating repetitive tasks like inventory updates, compliance checks, and report generation reduces manual effort and errors. Additionally, leveraging AI-driven analytics for predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, and decision support can significantly enhance asset performance- and lifecycle management.
For successful adoption, providing training sessions for relevant staff ensures proficiency in using the selected tools, while addressing any resistance and promoting a smooth adoption across the organization. Establishing a feedback loop to gather user input and continuously refine tools and processes is vital for continuous improvement. Regularly updating the tools to stay aligned with the latest technological advancements helps maintain efficiency and relevance.
Regular audits and assessments
Periodic reviews of the asset inventory and management practices are essential to ensure accuracy and compliance. The reviews help identify discrepancies and areas for improvement. By using audit findings to continuously refine and enhance the Asset Management process, organizations can maintain an up-to-date inventory, mitigate risks, and optimize resource utilization. This ongoing cycle of review and improvement is critical for sustaining an efficient and effective Asset and Configuration Management strategy.
Recognizing the positive effects of Asset and Configuration Management
Recognizing the positive effects of Asset and Configuration Management is pivotal in understanding its transformative impact on organizational security and operational efficiency. Effective asset and configuration management provides a comprehensive view of an organization’s IT landscape, ensuring that all hardware and software assets are accurately tracked and managed. This will support the organization, and uplift your cyber maturity and speed of execution across all cyber protection capabilities; be it identify, protect, detect, respond, recover, and govern/GRC.

Stronger security & reduced risk
By maintaining complete insight into your digital / technical landscape, organizations can achieve full understanding of all hardware and software assets within their network. The detailed inventory allows for meticulous tracking and management, ensuring no device or application goes unnoticed or unmanaged.
One of the significant advantages is the ease of patching. With an accurate and up-to-date asset list, vulnerabilities can be identified swiftly, enabling maintenance teams to apply necessary updates and patches promptly. A proactive approach ensures systems remain secure and resilient against potential exploits, effectively keeping organizations ahead of attackers.
Adding to this, maintaining thorough and current records aids in compliance. Regulatory requirements and internal policies often mandate detailed documentation of digital assets and their configurations. By adhering to the set standards, organizations not only avoid penalties but also builds trust with key stakeholders and senior management by demonstrating a commitment to maintaining secure and compliant operations.
Boosting efficiency & saving money
Effective Asset and Configuration Management optimizes resource allocation by eliminating redundancy and streamlining maintenance processes. This efficiency reduces IT headaches, as fewer problems arise from unmanaged assets, freeing operational teams to focus on strategic initiatives.
Informed decision-making is another key benefit, enabling data-driven choices regarding technology investments, lifecycle management, and capacity planning. This foresight ensures that the IT infrastructure can adapt to changing needs without disruptions, future-proofing the organization’s technological landscape.
Asset and Configuration Management empowers organizations with an insight into their technical and digital landscape, leading to stronger security, streamlined operations, and cost savings.
Final word
The adage ‘knowledge is power’ remains undeniably relevant in cybersecurity. Ensuring a consistent and robust approach to Asset and Configuration Management is a cornerstone that provides knowledge, enabling organizations to build resilient defenses against cyber threats. By embracing Asset and Configuration Management, organizations can achieve enhanced visibility & insight, reduced risk, and fortified security, ultimately safeguarding digital assets and ensuring business continuity. As the cyber threat landscape continue to evolve, so too must the strategies to counter them. With Asset and Configuration Management leading the charge in creating the foundational layer for establishing insight and ensuring the path for building cyber resilience to the appropriate level.

Further material
- The Axis cybersecurity reference guide (2) provides a comprehensive overview of cybersecurity concepts, including the importance of security configuration management. It defines security controls, which are safeguards used to minimize security risks, and highlights controls as a recommended set of best practices.
- The SaasAlerts article (3) further emphasizes the importance of security configuration management, explaining that misconfigurations and insecure default settings are a common gateway for cybercriminals. It outlines best practices for implementing security configuration management tools, such as tracking changes, testing early, and implementing multi-factor authentication.
- For additional cybersecurity framework guidance, the Theta article (4) recommends referencing the CIS Critical Security Controls and the New Zealand Information Security Manual (NZISM). These provide prescriptive advice on specific configurations and controls to enable (4).
- The Virima (5) and ABS Group (6) articles provide a deeper dive into the importance of robust cybersecurity asset management, including identifying all assets, and understanding their value.
Citations:
- Center for Internet Security – The 18 CIS Critical Security Controls (“CIS18”) https://www.cisecurity.org/controls/cis-controls-list
- Cybersecurity reference guide – Axis documentation https://help.axis.com/en-us/cybersecurity-reference-guide
- Why Is Configuration Management in Cybersecurity Important? https://saasalerts.com/why-is-configuration-management-in-cybersecurity-important/
- Which Cyber Security Framework Is Best for Your Business? – Theta https://www.theta.co.nz/post/which-cyber-security-framework-is-best-for-your-business
- Cybersecurity asset management: 10 things you must know – Virima https://virima.com/blog/cybersecurity-asset-management-10-things-you-must-know
- Cybersecurity Asset Management: What You Need To Know | ABS Group https://www.abs-group.com/Knowledge-Center/Insights/Cybersecurity-Asset-Management-What-You-Need-To-Know/
For further information please contact:

Latest articles & Updates